The development of the computer models of
plasma generators and accelerators working in the regime of the strong radiative-gas dynamic interaction
Main results
-
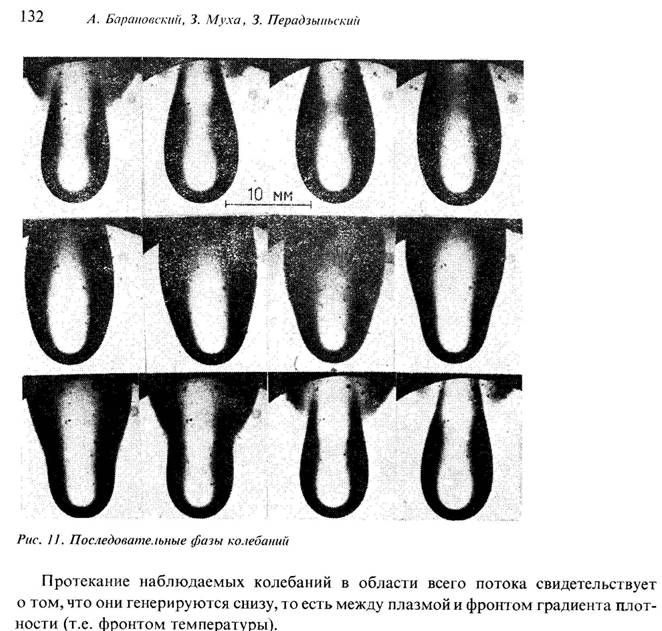
Theoretical and computational method reveal the new phenomena of self-oscillations
and bifurcations of subsonic gas flow in a localized area of energy release. The localized
energy release can be due to, e.g., absorption of a focused laser emission;
-
The computational models which predict the bifurcations of a gas flow (and help to
investigate this phenomena) are based on the Navier-Stokes system of equations and radiative heat transfer;
-
The phenomena of bifurcation means that at least two stable gasdynamic configuration
of gas flow aroung localized area of energy release exist;
-
There is a connection between the bifuraction phenomena and hysteresis phenomena. It
means that one of the gasdynamic structures remain stable when the power of energy release
gradually increases and the other remain stable when the power of energy release gradually decreases;
-
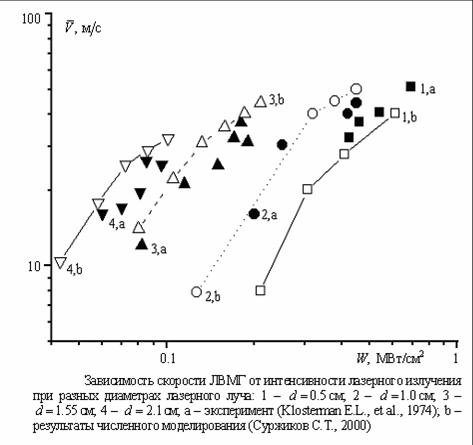
Theoretical and computational model of propagation velocity of subsonic radiative combustion
laser waves was created. The corresponding problem was solved. Qualitative agreement with the
experimental data were reached;
-
More informoation on the subject of research can be found in the book (in russian):
Surzhikov S.T. Physical mechanics of gas discharges,
Moscow: BMSTU publishing, 2006, 640 p. (Computer models of physical mechanics).
The phenomena of the laser plasma instability
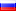
Laser plasma generator
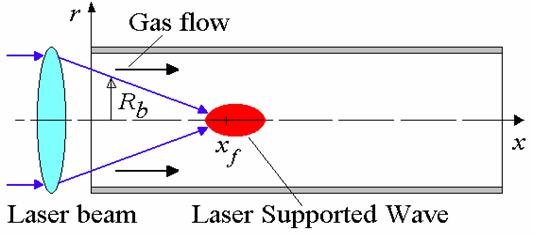 |
- Navier-Stokes equations;
- Models of turbulent mixing;
- 11-component mixture of chemically reacting air;
- Multigroup model of thermal radiation.
|
The instability of laser combustion wave in free space
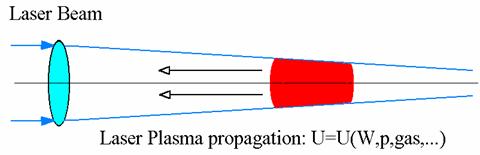 |
- Navier-Stokes equations;
- Models of turbulent mixing;
- 11-component mixture of chemically reacting air;
- Multigroup model of thermal radiation.
|
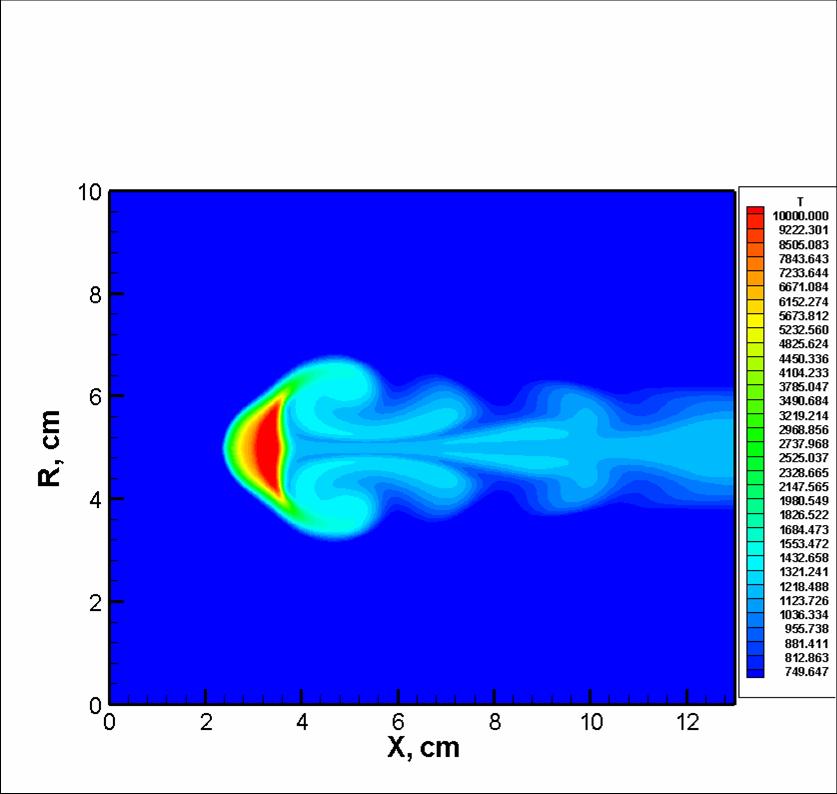
Results of numerical simulation
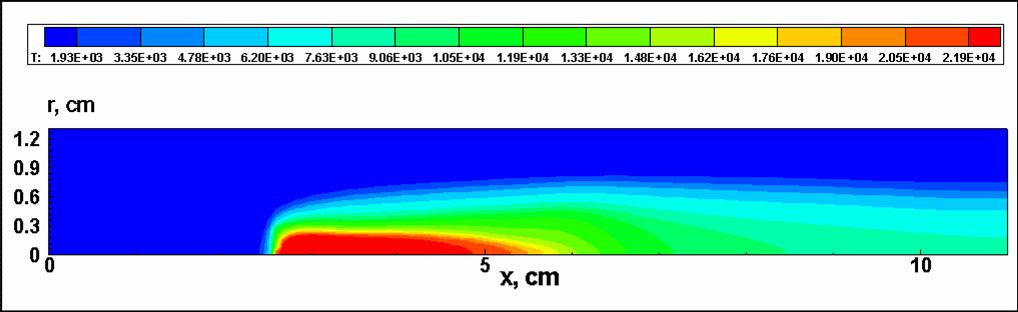
The instability of the laser plasma in the subsonic flow, U0 = 30 m/s, P = 100 kW, air
The experimental data on the propagation velocity of the laser plasma and examples of the numerical calculations
Laser combustion wave propagation in heat-conducting mode (some experimental data)
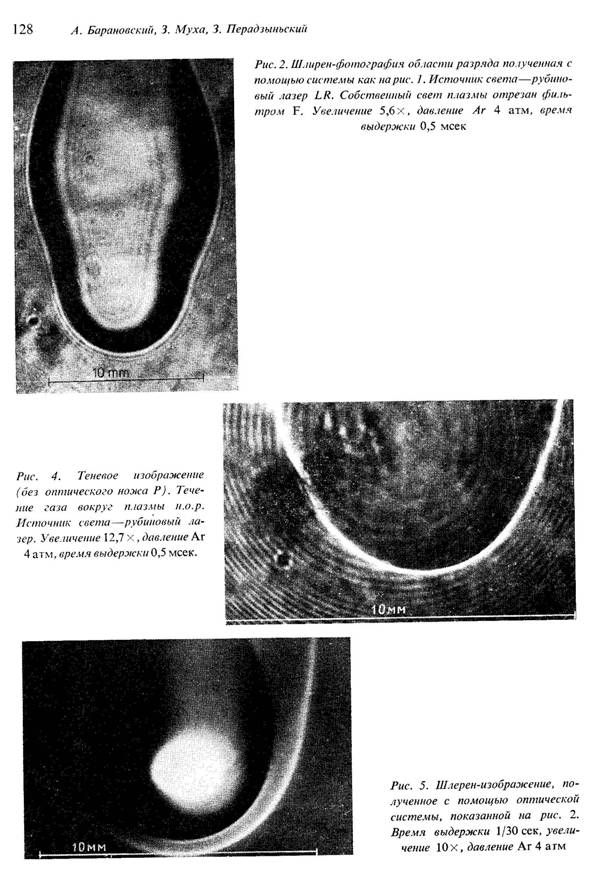
Experimental evidence of self-oscillations of the laser plasma